1St Ionization Energy Chart
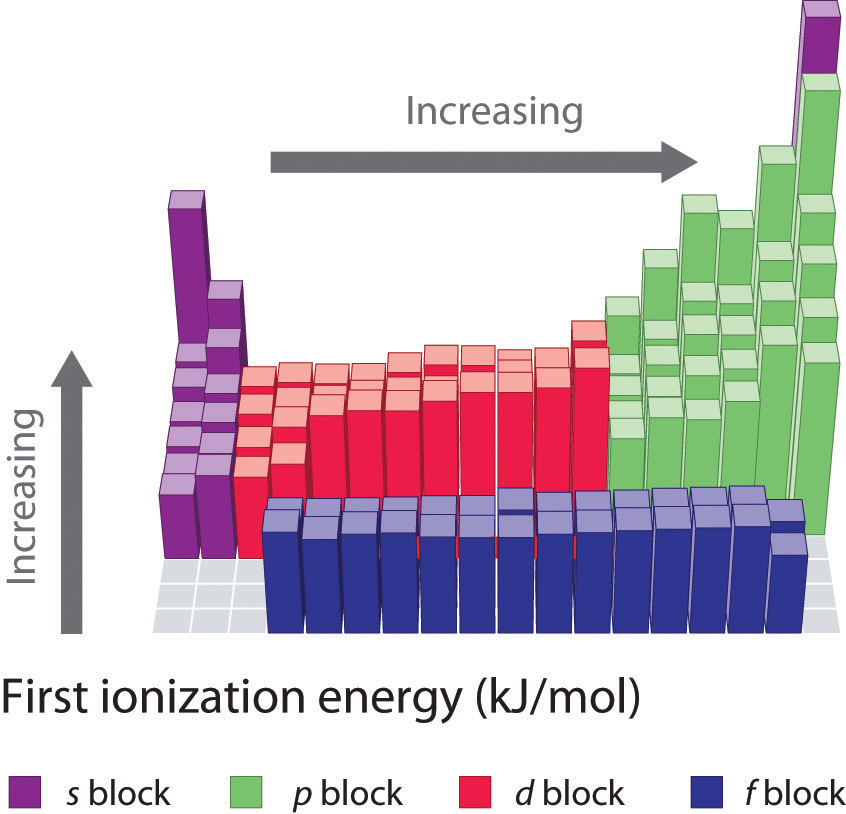
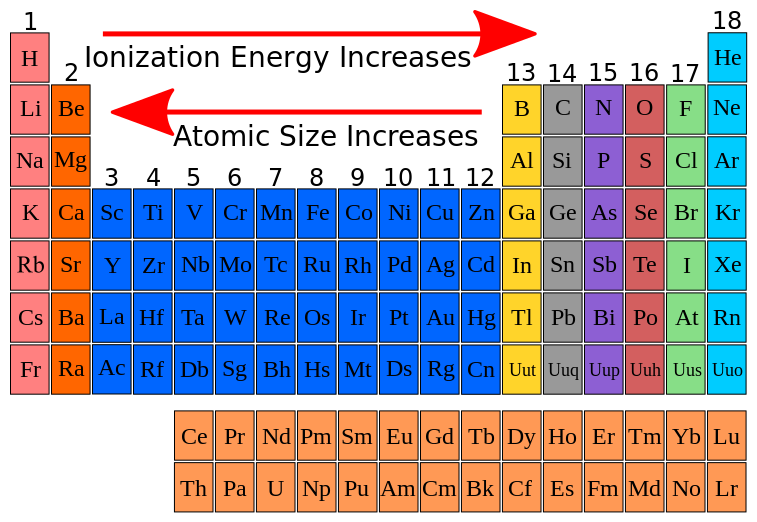
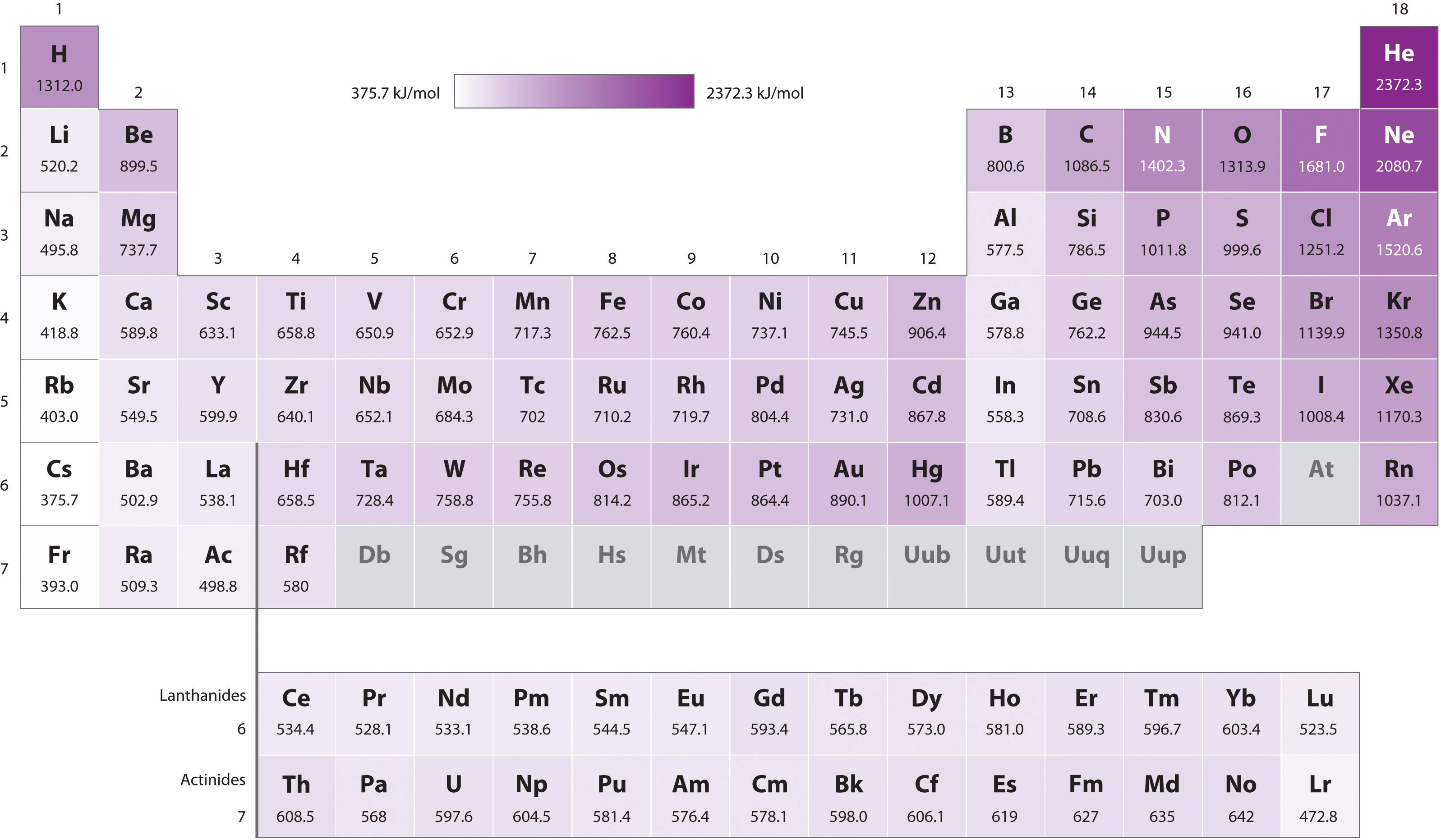
1St Ionization Energy Chart - Web oxygen’s first ionization energy is 1313.9 kj/mol, while carbon is 1086.5 kj/mol. Web for each atom, the column marked 1 is the first ionization energy to ionize the neutral atom, the column marked 2 is the second ionization energy to remove a second electron from the +1 ion, the column marked 3 is the third ionization energy to remove a third electron from the +2 ion, and so on. Sure it has another paired p electron, but it also has more protons than the previous elements in the same period. Web in the equation, the “first ionization energy” refers to the ionization energy required to remove a neutral atom’s first electron, giving an ion with a single positive charge. Fluorine has a high first ionization energy because it has such a high effective nuclear charge. The graph shows how the first ionisation energy varies across period 3. Each succeeding ionization energy is larger than the preceding energy. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. An element's second ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a 1+ ion of the element. Web the symbol i1 i 1 stands for the first ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from a neutral atom, where n = 0 n = 0 ). This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry. Web first ionisation energy is the enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms forms one mole of gaseous ions with. Web the first ionisation energy is the energy required to remove one mole of the most loosely held electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms to produce 1 mole of gaseous ions each with a charge of 1+. Ionization energy increases moving across a period and decreases moving down a group. Explain the reason for the variation in first ionization. Web these tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. Web the symbol \(i_1\) stands for the first ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from a neutral atom) and the symbol \(i_2\) stands for the second ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from an atom with a +1 charge. A general. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. The amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from a gaseous atom in its ground state is called its first ionization energy (ie 1). Web for each atom, the column marked 1 is the first ionization energy to ionize the neutral atom, the column marked 2. Web webelements periodic table » periodicity » ionization energy: The elements of the periodic table sorted by ionization energy. Explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web in the equation, the “first ionization energy” refers to the ionization energy required to remove a neutral atom’s first electron, giving an ion. Explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Web oxygen’s first ionization energy is 1313.9 kj/mol, while carbon is 1086.5 kj/mol. The amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from a gaseous atom in its ground state is called its first ionization energy (ie 1). The graph. And (b) oxygen through tellurium in group 16. Explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. Because positive charge binds electrons more strongly, the second ionization energy of an element is always higher than the first. Web the symbol i1 i 1 stands for the first ionization energy (energy required to. Web use the values of the first ionization energies given in figure 3.3.3 to construct plots of first ionization energy versus atomic number for (a) boron through oxygen in the second period; Which plot shows more variation? Web first ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. The second. First ionization energy increase from left to right and from bottom to top. Web ionization energy is denoted by the symbols ie, ip, δh° and has units of kilojoule per mole ( (kj/mol) or electron volts (ev). A general equation for this enthalpy change is: It measures the capability of an atom to lose an electron during a chemical reaction.. Sure it has another paired p electron, but it also has more protons than the previous elements in the same period. Which plot shows more variation? This is more easily seen in symbol terms. This is more easily seen in symbol terms. It measures the capability of an atom to lose an electron during a chemical reaction. And (b) oxygen through tellurium in group 16. Web x (g) + energy x + (g) + e −. It is an endothermic process, i.e. Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom or ion. Web the first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from one mole of neutral gaseous atoms to produce 1 mole of gaseous ions each with a charge of 1+. Ionization energy increases moving across a period and decreases moving down a group. Web first ionisation energy is the enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms forms one mole of gaseous ions with a single positive charge. Web use the values of the first ionization energies given in figure 3.3.3 to construct plots of first ionization energy versus atomic number for (a) boron through oxygen in the second period; Web these tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. Which plot shows more variation? Web in the equation, the “first ionization energy” refers to the ionization energy required to remove a neutral atom’s first electron, giving an ion with a single positive charge. Web oxygen’s first ionization energy is 1313.9 kj/mol, while carbon is 1086.5 kj/mol. The first ionization energy for an element, x, is. The 1st ionization energy of the element m is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of the gaseous atoms m. Web the symbol \(i_1\) stands for the first ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from a neutral atom) and the symbol \(i_2\) stands for the second ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from an atom with a +1 charge. This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry.
Ionization energy Definition & Facts Britannica
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy Chemistry Socratic
7.4 Ionization Energy Chemistry LibreTexts
FileIonization energy atomic size.svg Wikimedia Commons

Ionization Energy Definition, Chart & Periodic Table Trend

Quick Notes (revision) for ASLevel ChemistryStudent
Periodic Trends in Ionization Energy CK12 Foundation
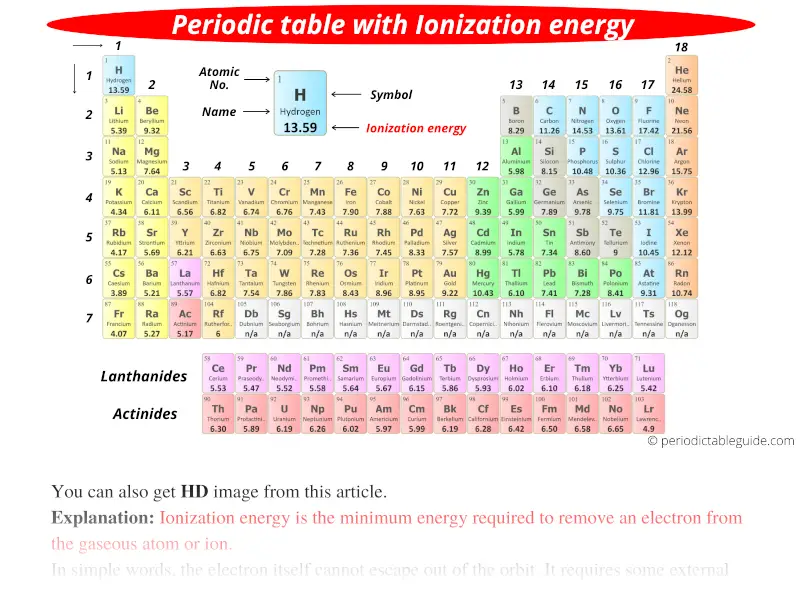
Periodic table with Ionization Energy Values (Labeled Image)

Periodic Properties of the Elements Chemwiki
6.6 Ionization Energies Chemistry LibreTexts
The Second Ionisation Energy ( Ie2) Is The Energy Required To Remove The Second Mole Of Electrons From Each +1 Ion In A Mole Of Gaseous +1 Ions, To Form One Mole Of +2 Ions.
Sure It Has Another Paired P Electron, But It Also Has More Protons Than The Previous Elements In The Same Period.
This Is More Easily Seen In Symbol Terms.
Web The Symbol I1 I 1 Stands For The First Ionization Energy (Energy Required To Take Away An Electron From A Neutral Atom, Where N = 0 N = 0 ).
Related Post:
